Wednesday, February 7, 2007

Effects of Oxytocin on Females
In years past, oxytocin had the reputation of being an "uncomplicated" hormone, with only a few well-defined activities related to birth and lactation. As has been the case with so many hormones, further research has demonstrated many subtle but profound influences of this little peptide. Nevertheless, it has been best studied in females where it clearly mediates three major effects:
Stimulation of milk ejection (milk letdown): Milk is initially secreted into small sacs within 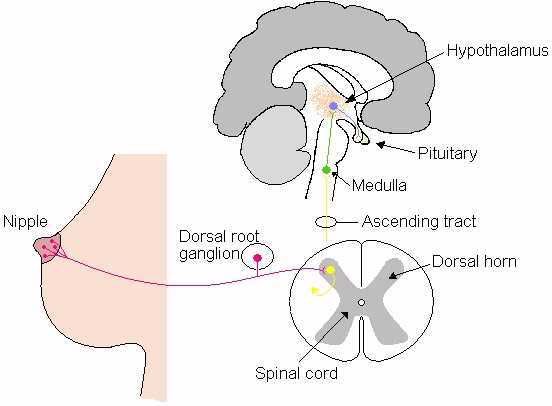 the mammary gland called alveoli, from which it must be ejected for consumption or harvesting. Mammary alveoli are surrounded by smooth muscle (myoepithelial) cells which are a prominant target cell for oxytocin. Oxytocin stimulates contraction of myoepithelial cells, causing milk to be ejected into the ducts and cisterns.
the mammary gland called alveoli, from which it must be ejected for consumption or harvesting. Mammary alveoli are surrounded by smooth muscle (myoepithelial) cells which are a prominant target cell for oxytocin. Oxytocin stimulates contraction of myoepithelial cells, causing milk to be ejected into the ducts and cisterns.
Stimulation of uterine smooth muscle contraction at birth: At the end of gestation, the uterus must contract vigorously and for a prolonged period of time in order to deliver the fetus. During the later stages of gestation, there is an increase in abundance of oxytocin receptors on uterine smooth muscle cells, which is associated with increased "irritability" of the uterus (and sometimes the mother as well). Oxytocin is released during labor when the fetus stimulates the cervix and vagina, and it enhances contraction of uterine smooth muscle to facilitate parturition or birth.
In cases where uterine contractions are not sufficient to complete delivery, physicians and veterinarians sometimes administer oxytocin ("pitocin") to further stimulate uterine contractions - great care must be exercised in such situations to assure that the fetus can indeed be delivered and to avoid rupture of the uterus.
 Establishment of maternal behavior: Successful reproduction in mammals demands that mothers become attached to and nourish their offspring immediately after birth. It is also important that non-lactating females do not manifest such nurturing behavior. The same events that affect the uterus and mammary gland at the time of birth also affect the brain. During parturition, there is an increase in concentration of oxytocin in cerebrospinal fluid, and oxytocin act
Establishment of maternal behavior: Successful reproduction in mammals demands that mothers become attached to and nourish their offspring immediately after birth. It is also important that non-lactating females do not manifest such nurturing behavior. The same events that affect the uterus and mammary gland at the time of birth also affect the brain. During parturition, there is an increase in concentration of oxytocin in cerebrospinal fluid, and oxytocin act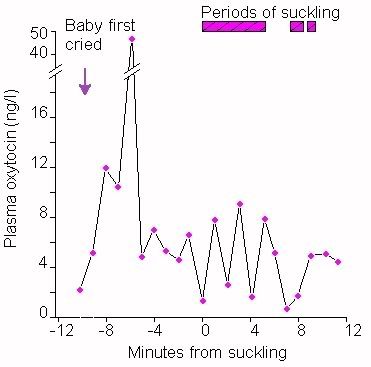 ing within the brain plays a major role in establishing maternal behavior.Evidence for this role of oxytocin come from two types of experiments. First, infusion of oxytocin into the ventricles of the brain of virgin rats or non-pregnant sheep rapidly induces maternal behavior. Second, administration into the brain of antibodies that neutralize oxytocin or of oxytocin antagonists will prevent mother rats from accepting their pups. Other studies support the contention that this behavioral effect of oxytocin is broadly applicable among mammals.
ing within the brain plays a major role in establishing maternal behavior.Evidence for this role of oxytocin come from two types of experiments. First, infusion of oxytocin into the ventricles of the brain of virgin rats or non-pregnant sheep rapidly induces maternal behavior. Second, administration into the brain of antibodies that neutralize oxytocin or of oxytocin antagonists will prevent mother rats from accepting their pups. Other studies support the contention that this behavioral effect of oxytocin is broadly applicable among mammals.
While all of the effects described above, doubt has recently been cast on its necessity in parturition and maternal behavior. Mice that are unable to secrete oxytocin due to targeted disruptions of the oxytocin gene will mate, deliver their pups without apparent difficulty and display normal maternal behavior. However, they do show deficits in milk ejection and have subtle derangements in social behavior. It may be best to view oxytocin as a major facilitator of parturition and maternal behavior rather than a necessary component of these processes.
6:13 PM
let our love blossom this valentine..
